Laurie Anne Walden, DVM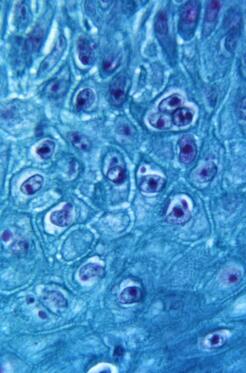 Monkeypox virus particles in skin from an infected monkey (900× magnification). Public domain image from CDC, 1968. Monkeypox virus particles in skin from an infected monkey (900× magnification). Public domain image from CDC, 1968. Monkeypox is a zoonotic disease; it spreads between animals and humans. In the United States, the chance that a person will catch monkeypox from a pet or give monkeypox to a pet is very low. Transmission between people and pets is possible, though, so the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has developed monkeypox guidance for pet owners. This article summarizes information from the CDC and the American Veterinary Medical Association (AVMA) and is current as of August 24, 2022. See these links for updates:
How Monkeypox Spreads Monkeypox was first discovered in 1958 in monkeys and since then has been found in many animal species. Rodents and other small mammals (not monkeys) are thought to be the reservoir species that maintain the virus. Human infection was first reported in 1970 in Africa, and monkeypox has occasionally appeared in other parts of the world. The United States had an outbreak in 2003 after pet prairie dogs were housed with infected animals from Ghana. The 2022 global monkeypox outbreak has involved at least 75 countries. The monkeypox virus is related to the virus that causes smallpox. The virus infects the host through the respiratory tract, mouth, eyes, or broken skin. These are some of the ways people and animals are infected:
Most transmission during the 2022 outbreak has been through close, direct contact with an infected person. Animals at Risk One pet dog has contracted monkeypox, most likely from direct contact with its owners (this was the first reported case of human-to-animal transmission). Chinchillas, prairie dogs, and some types of rabbits, mice, and rats can be infected with the monkeypox virus. Many wild mammals are also susceptible to infection. Cats, guinea pigs, hamsters, and cows can be infected with other viruses in the same genus as monkeypox, but whether they can also be infected with the monkeypox virus is not yet known. The CDC says that it’s best to assume that any mammal can be infected. There have been no reports of infection in animals that are not mammals. Signs of Monkeypox in Animals These are some of the signs that infected animals have developed:
These symptoms are nonspecific. Many conditions that are much more common than monkeypox cause the same symptoms in animals. Diagnosing monkeypox requires laboratory tests. Precautions for Pet Owners: CDC Guidance
If You Think Your Pet Has Monkeypox: CDC Guidance
Sources Monkeypox. American Veterinary Medical Association. Accessed August 24, 2022. https://www.avma.org/resources-tools/one-health/veterinarians-and-public-health/monkeypox Monkeypox in animals. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated August 17, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/veterinarian/monkeypox-in-animals.html Monkeypox: pets in the home. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updated August 17, 2022. Accessed August 24, 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/poxvirus/monkeypox/specific-settings/pets-in-homes.html Seang S, Burrel S, Todesco E, et al. Evidence of human-to-dog transmission of monkeypox virus. Lancet. 2022:S0140-6736(22)01487-8. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01487-8 Image source: CDC Comments are closed.
|
AuthorLaurie Anne Walden, DVM Categories
All
Archives
June 2024
The contents of this blog are for information only and should not substitute for advice from a veterinarian who has examined the animal. All blog content is copyrighted by Mallard Creek Animal Hospital and may not be copied, reproduced, transmitted, or distributed without permission.
|
- Home
- About
- Our Services
- Our Team
-
Client Education Center
- AKC: Spaying and Neutering your Puppy
- Animal Poison Control
- ASPCA Poisonous Plants
- AVMA: Spaying and Neutering your pet
- Biting Puppies
- Boarding Your Dog
- Caring for the Senior Cat
- Cats and Claws
- FDA warning - Bone treats
- Force Free Alliance of Charlotte Trainers
- Getting your Cat to the Vet - AAFP
- Holiday Hazards
- How To Feed Cats for Good Health
- How to Get the Most Out of your Annual Exam
- Indoor Cat Initiative - OSU
- Introducing Your Dog to Your Baby
- Moving Your Cat to a New Home
- Muzzle Training
- Osteoarthritis Checklist for Cats
- What To Do When You Find a Stray
- Our Online Store
- Dr. Walden's Blog
- Client Center
- Contact
- Cat Enrichment Month 2024
|
Office Hours
Monday through Friday 7:30 am to 6:00 pm
|
Mallard Creek Animal Hospital
2110 Ben Craig Dr. Suite 100
|
Site powered by Weebly. Managed by IDEXX Laboratories

 RSS Feed
RSS Feed